Defibrillation Procedure
Lesson Progress
0% Complete
WHAT IS THE DEFIBRILLATION PROCEDURE?
Defibrillation is a process in which an electrical device called a defibrillator sends an electric shock to the heart to stop an arrhythmia resulting in the return of a productive heart rhythm. Purpose Defibrillation is performed to correct life-threatening arrhythmias of the heart including ventricular fibrillation and cardiac arrest. In cardiac emergencies it should be performed immediately.
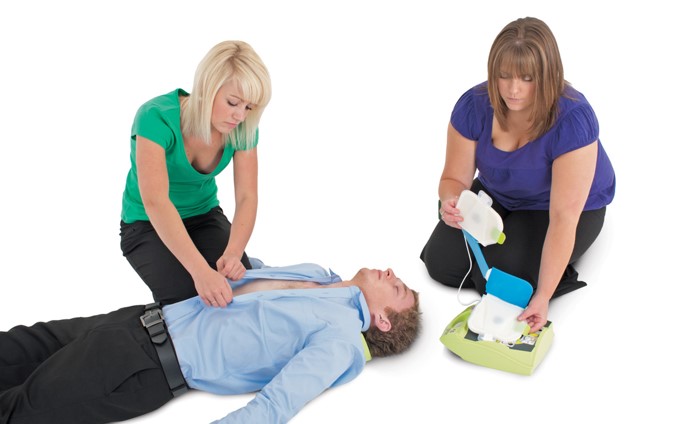
- when the Defibrillator (Automated External Defibrillation) arrives, you must immediately unpack it and prepare to fix the pads to the casualty.
- If you have trained help, then allow them to continue with CPR until you are ready.
- if not, then stop CPR and unpack it yourself.
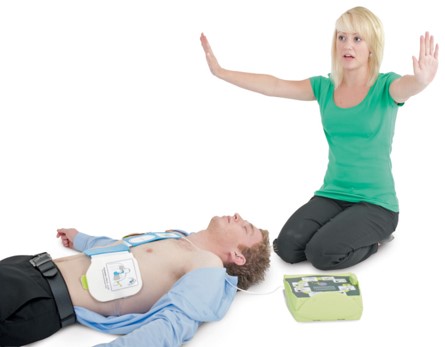
- It is important from here on in to follow the voice prompts as soon as the pads are connected and the AED is switched on.
- If the AED voice prompts you to shock the casualty, ensure everyone is clear before pressing the shock button.
- if you are prompted to commence CPR then quality CPR is important
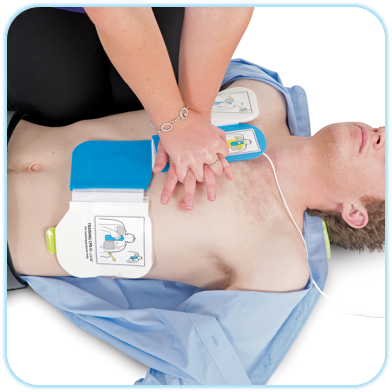
- ensure that you compress at the right depth and at the right speed
Here are the details of how deep and fast you should do chest compressions:

PAEDIATRIC DEFIBRILLATION FOR CHILDREN & INFANTS
- Most manufacturers will have specially designed pads for defibrillating children.
- Generally speaking a child is deemed as being from the age of 1 to 8, or up to 25kg in weight (55lbs).
- Any young person aged from 8 upwards, should be treated as an adult for the purposes of defibrillation.
- A you know from an earlier module an infant is aged from birth to 1 year old – some AED manufacturers will be able to provide pads for this age group. You would need to check with your suppliers.

